Neuroscience of learning and memory processes explained
Anúncios
The neuroscience of learning and memory processes reveals that emotions significantly impact learning, and effective strategies like repetition, active engagement, and mnemonic devices enhance memory retention.
The neuroscience of learning and memory processes reveals how our brains adapt and store information. Curious about the inner workings of your mind? Let’s dive deeper into this intriguing topic.
Anúncios
Understanding the fundamentals of neuroscience
Understanding the basics of neuroscience is essential for grasping how we learn and remember. Neuroscience explores the complex workings of the brain and nervous system, which are crucial for cognitive functions.
Neuroscience is the study of how the brain works. This field examines the structure of the brain and the roles different parts play in learning and memory. It integrates science from biology, psychology, and even computer science to provide a comprehensive picture of how we acquire knowledge.
The brain’s structure and its functions
The brain is divided into several regions, each responsible for specific tasks. Understanding these areas can deepen our knowledge of learning and memory processes. Here are some key regions:
Anúncios
- Cerebral cortex: Involved in critical thinking and decision-making.
- Hippocampus: Essential for forming new memories.
- Amygdala: Plays a role in emotional responses.
- Thalamus: Acts as a relay station for sensory information.
The connection between these brain areas is vital for efficient learning. For example, when we learn something new, the hippocampus helps store that information while the amygdala links it to emotions, enhancing memory retention.
Neurons and synapses
Neurons are the building blocks of the brain. They transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. When learning occurs, synapses, or connections between neurons, strengthen, affecting how we remember what we’ve learned.
This phenomenon is known as synaptic plasticity. As we practice or engage with new information, these synapses become more robust, making retrieval easier over time.
Exploring the connection between neurons provides insight into how memories are formed and recalled. The more connections made, the easier it is for the brain to retrieve that information later.
In summary, understanding the fundamentals of neuroscience unveils how our brain functions. This knowledge empowers us to develop strategies for better learning and memory retention.
The role of neuroplasticity in learning
The concept of neuroplasticity is crucial in understanding how we learn and adapt. It refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This remarkable feature allows us to modify and strengthen our learning processes.
When we engage in new activities or learn new information, our brains change structurally and functionally. Neuroplasticity happens at different levels, from the cellular level to entire regions of the brain. This means that our experiences shape our brain, making it adaptable over time.
How neuroplasticity supports learning
Neuroplasticity plays a vital role in several aspects of learning:
- Skill acquisition: As we practice a skill, the neural pathways involved in that skill become stronger, leading to better performance.
- Memory formation: When we learn something new, the brain creates new connections, helping us store that information more effectively.
- Recovery from injury: Neuroplasticity allows brain regions to take over functions that may have been lost due to injury.
- Emotional resilience: Adapting and changing our neural pathways can help us manage stress and emotions better.
The ability to learn is linked to our potential for change. Therefore, engaging in diverse activities can enhance this adaptability. Learning a new language, playing a musical instrument, or even solving puzzles can stimulate neuroplasticity.
Strategies to enhance neuroplasticity
There are effective strategies to promote neuroplasticity in learning. These include:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, enhancing its capacity to adapt.
- Mental challenges: Activities that require concentration and thought can stimulate new connections.
- Mindfulness practices: Techniques such as meditation can positively affect brain structure and function.
- Social interactions: Engaging with others can lead to enriching experiences and learning opportunities.
By adopting these strategies, individuals can enhance their learning capabilities. Embracing change and new experiences is essential for fostering neuroplasticity. This ongoing process is what makes learning an exciting and lifelong journey.
Memory formation: processes and stages
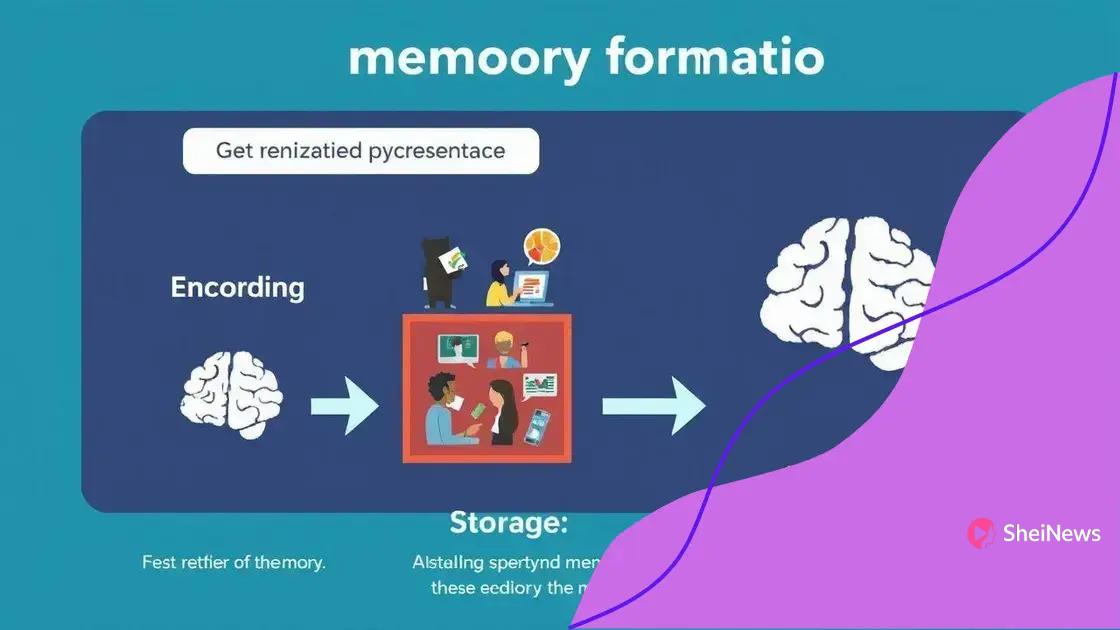
Memory formation is a fascinating process involving several stages. It allows us to learn, recall events, and build knowledge over time. Understanding how memories are formed helps us improve learning techniques and enhances our ability to retain information.
The process of forming memories can be divided into three main stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Each stage plays a crucial role in how we remember things.
Encoding: The first step
Encoding is where the process begins. When we experience something new, our brain transforms this information into a format that can be stored. This can happen through:
- Visual encoding: Forming a mental picture of what we see.
- Acoustic encoding: Processing sounds and acquiring language.
- Semantic encoding: Understanding the meaning of what we learn.
These methods help us create connections that enhance memory retention. The more effectively we encode information, the easier it will be to recall it later.
Storage: Keeping memories safe
After encoding, the next step is storage. This stage involves maintaining information over time and can be categorized into:
- Short-term memory: Holds limited information for a brief period.
- Long-term memory: Capable of storing vast amounts of information for extended periods, sometimes a lifetime.
Memories are stored in different types, such as episodic (personal experiences) and semantic (facts and concepts). The brain utilizes various structures, including the hippocampus, to organize and store these memories effectively.
Retrieval: Accessing stored memories
Retrieval is the final stage in memory formation, enabling us to access stored information when needed. This can happen through:
- Recall: Retrieving information without cues, such as answering a question.
- Recognition: Identifying previously encountered information, like multiple-choice questions.
Effective retrieval relies on strong connections established during the encoding process. The more familiar and connected the information is, the easier it becomes to access it later.
Understanding memory formation involves recognizing how each stage works together to contribute to our learning and recall abilities. By enhancing encoding practices, improving storage techniques, and developing effective retrieval strategies, we can boost our overall memory performance.
How emotions impact learning
Emotions play a significant role in the way we learn. When we engage with information, our emotional state can influence memory retention, motivation, and overall learning effectiveness. Understanding how emotions affect learning can help us create better educational environments.
Research shows that positive emotions enhance learning by boosting motivation and focus. When students are excited or happy, they are more likely to engage with the material. These emotions also promote better memory formation, making it easier to recall information later.
The impact of negative emotions
On the other hand, negative emotions like fear, anxiety, and stress can hinder the learning process. Stress can lead to difficulty concentrating and can interfere with memory retrieval. For instance, students who feel anxious during tests may struggle to recall what they studied.
Managing negative emotions is crucial for effective learning. Strategies such as mindfulness, relaxation techniques, and positive reinforcement can help students feel more secure and open to learning.
Emotion regulation in learning
Emotion regulation is the ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences. This skill is essential in educational settings. Students who can effectively regulate their emotions are often more successful learners. They can maintain motivation and focus, even in challenging situations.
- Self-awareness: Understanding one’s emotional triggers helps in managing feelings.
- Mindfulness practices: Techniques like meditation can improve emotional control.
- Supportive environments: Learning in a safe space encourages emotional expression and reduces stress.
Incorporating emotional awareness into learning strategies can significantly enhance outcomes. Teachers and educators can foster emotional intelligence, encouraging students to recognize and express their feelings. By prioritizing emotional health, we create an atmosphere conducive to learning.
Ultimately, recognizing the impact of emotions on learning allows us to develop techniques that support both cognitive and emotional growth. This holistic approach leads to better retention, increased engagement, and a more fulfilling educational experience.
Strategies to enhance memory retention
Enhancing memory retention is crucial for effective learning. There are several strategies that anyone can implement to improve their ability to remember information. These techniques help reinforce knowledge and make it easier to recall when needed.
One effective approach is to use repetition. When you review material multiple times, it allows your brain to strengthen the neural connections associated with that information. This process makes it easier to retrieve later on.
Utilizing mnemonic devices
Mnemonic devices are clever strategies that aid in memory retention. They help organize information in a way that is easier to remember. Some common types include:
- Acrostics: Using the first letters of words to create a phrase.
- Rhymes: Crafting a catchy rhyme that incorporates the information.
- Visualization: Creating mental images to represent concepts.
By associating new information with familiar images or phrases, you can create stronger memory connections.
Active engagement with material
Another strategy is active engagement with the learning material. This means interacting with the content rather than passively reading it. For example, you can:
- Summarize: Write summaries of what you’ve learned.
- Teach someone else: Explaining concepts to others reinforces your understanding.
- Use flashcards: Testing yourself helps to retrieve information actively.
These activities promote deeper processing, leading to better retention. Engaging actively with the material can transform how you remember it.
Another effective technique is organizing information into chunks. This approach breaks down large amounts of information into smaller, manageable units. For instance, remembering a long number can be easier if you group digits together. This strategy minimizes cognitive overload and enhances recall.
Additionally, ensuring good sleep and maintaining a healthy diet can significantly improve memory functions. Sleep plays a vital role in memory consolidation, while certain foods can support brain health and cognitive performance.
In conclusion, understanding the neuroscience of learning and memory processes opens doors to better educational practices and personal growth. By knowing how emotions impact learning, we can enhance strategies to improve memory retention. Techniques like active engagement, repetition, and the use of mnemonic devices are effective ways to strengthen our ability to remember information. Additionally, nurturing emotional health and adopting effective learning strategies will lead to a more successful educational experience. Embrace these insights to unlock your full potential in learning!
\n\n
\n
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about the Neuroscience of Learning and Memory
How do emotions affect learning?
Emotions play a crucial role in learning by influencing motivation and memory retention. Positive emotions enhance engagement, while negative emotions can hinder learning.
What strategies can help improve memory retention?
Some effective strategies include using repetition, mnemonic devices, and active engagement with the material. Organizing information into chunks also helps enhance recall.
Why is sleep important for memory?
Sleep is essential for memory consolidation. During sleep, the brain processes and organizes information, making it easier to recall later.
How can I create a supportive learning environment?
Fostering a supportive learning environment involves encouraging emotional expression, reducing stress, and promoting active engagement with the material.





